Extrachromosomal MET Amplification Spurs Drug Resistance in ROS1+ NSCLC
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a genetically heterogeneous disease. In approximately 2% of NSCLC cases, the primary oncogenic mutation is a chromosomal rearrangement involving ROS1 (ROS proto-oncogene 1), where one of many diverse gene partners fuses to the 3’ kinase domain of ROS1 and results in the constitutive activation of the ROS1 receptor tyrosine kinase. The ROS1-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) entrectinib is an FDA-approved treatment for patients with these ROS1 fusions (ROS1+ NSCLC) and has dramatically improved patient outcomes...

Known Cancer Driver Mutations Found in Endometrial Polyps at Low Allelic Frequencies
Endometrial polyps (EMPs) are localized overgrowths of endometrial tissue composed of endometrial glands, stroma, and blood vessels. The reported prevalence of EMPs increases with age and ranges from 8-35%, depending on the population studied. EMPs are considered benign, with a risk of malignancy of around 3%...

Cerebrovascular β-Amyloid Deposits Linked to Altered Gene Expression Profile in Mice with Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in older adults. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), which is characterized by the deposition of β-amyloid (Aβ) peptides within cerebral blood vessels, co-occurs with AD to some extent in 85-95% of AD cases and is an independent contributor to AD dementia. Indeed, cerebrovascular dysfunction, possibly resulting from Aβ deposits, has been implicated in early AD pathogenesis, preceding neuronal damage...

Loss of TP53 Promotes NEK2 Amplification, Spurring Multiple Myeloma Aggressiveness
In the broadest sense, cancer development is spurred by genetic abnormalities that result in oncogene activation and tumor suppressor gene inactivation. In multiple myeloma (MM), a hematological malignancy that affects plasma cells, the amplification of chromosome 1q and the deletion of chromosome 17p have both been shown to be related to disease progression and poor patient outcomes. Chromosome 1q contains several oncogenes including NEK2 (never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 2), which has been shown to promote tumor cell proliferation, metastasis, and drug resistance in MM and other cancer types...

New Oncogenic Mechanism Proposed for Basal-like Breast Cancer
The aggressive basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) subtype, which strongly correlates with triple-negative (ER- PR- HER2-) breast cancers, comprises 15-20% of all breast cancer cases and has a poor prognosis, largely resulting from a lack of a molecularly targeted treatment regimen. Loss of control of signaling pathways frequently triggers tumorigenesis, and molecules involved in these signaling pathways are frequent molecular treatment targets. However, the mechanisms of tumorigenesis in BLBCs have yet to be fully elucidated. ..

Lorlatinib is Effective in Targeting Novel CLIP1-LTK Fusion in Lung Cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common form of lung cancer and a leading cause of death worldwide. Fortunately, the survival rate for NSCLC patients has been increasing, largely due to advances in targeted molecular and immunotherapies. Somatic mutations ..

Pembrolizumab Post-AlloHCT Most Beneficial for PD-L1 Amplified Lymphomas
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT) is used to treat a variety of hematologic malignancies and represents the best chance for cure for many patients with these disorders. The effectiveness of alloHCT relies primarily on graft-versus-tumor (GVT) reactivity facilitated by donor T cells, which ..

PROTAC Resistance in Cancer Cells is Mediated by MDR1 Drug Efflux Activity
Selectively inhibiting protein function through proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) has emerged as a novel cancer therapeutic strategy. PROTACs are small molecules with two active domains that bind to an E3 ubiquitin ligase and a protein of interest, which results in..

Loss of Chromosome Y Linked to AML and Clonal Hematopoiesis
Mosaic loss of chromosome Y (mLOY) is the most common form of clonal mosaicism and is recurrent in the blood cells of adult males. This chromosome alteration typically increases with age and has ..

HER2+ Breast Cancers with CDR2L Alterations Most Likely to Develop Paraneoplastic Syndrome
Paraneoplastic syndromes are rare disorders co-occurring with cancer that are not directly related to the local presence of tumor cells, but result from the generation of autoantibodies, cytokines, hormones, or peptides in response to the malignancy...

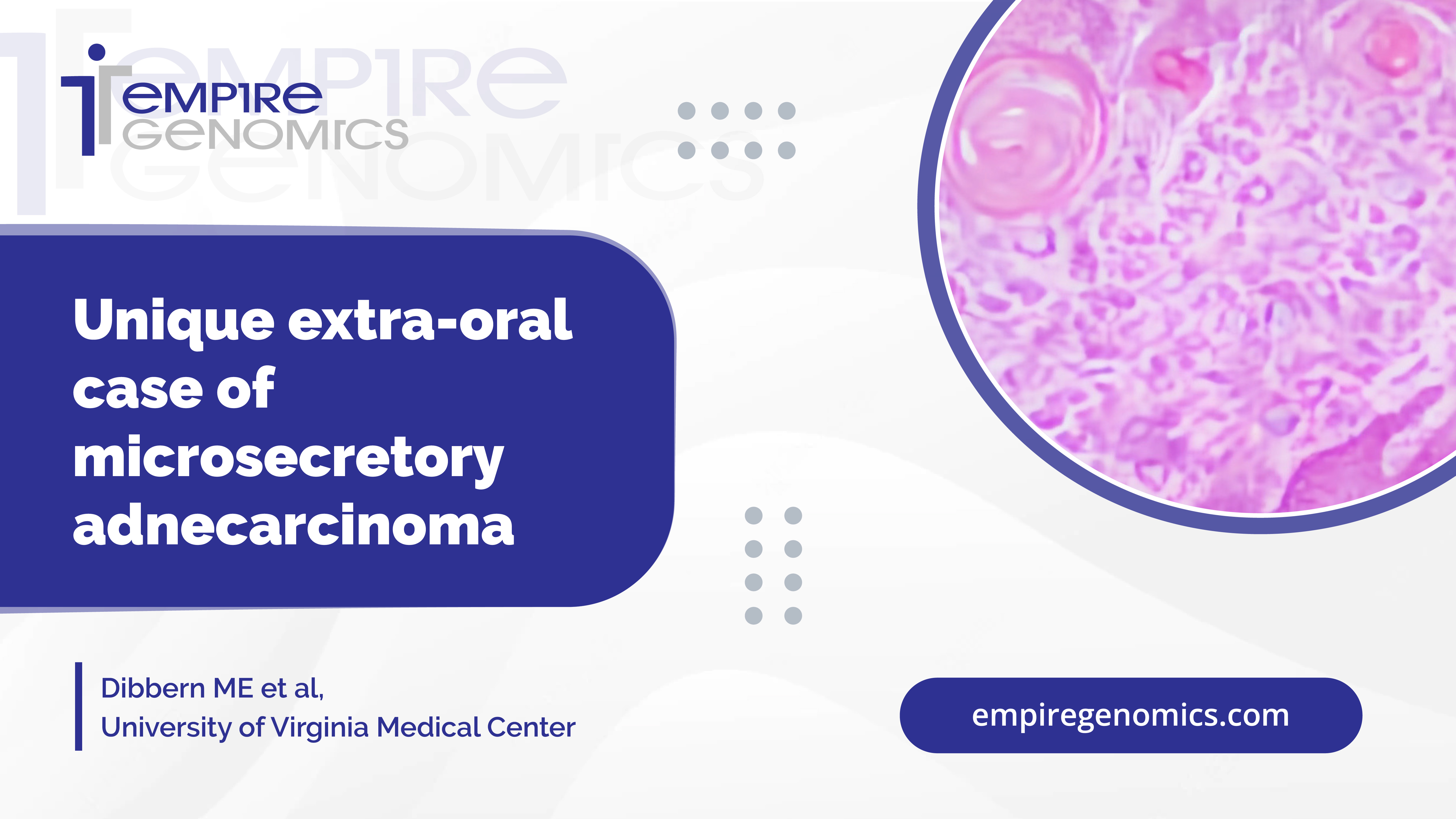
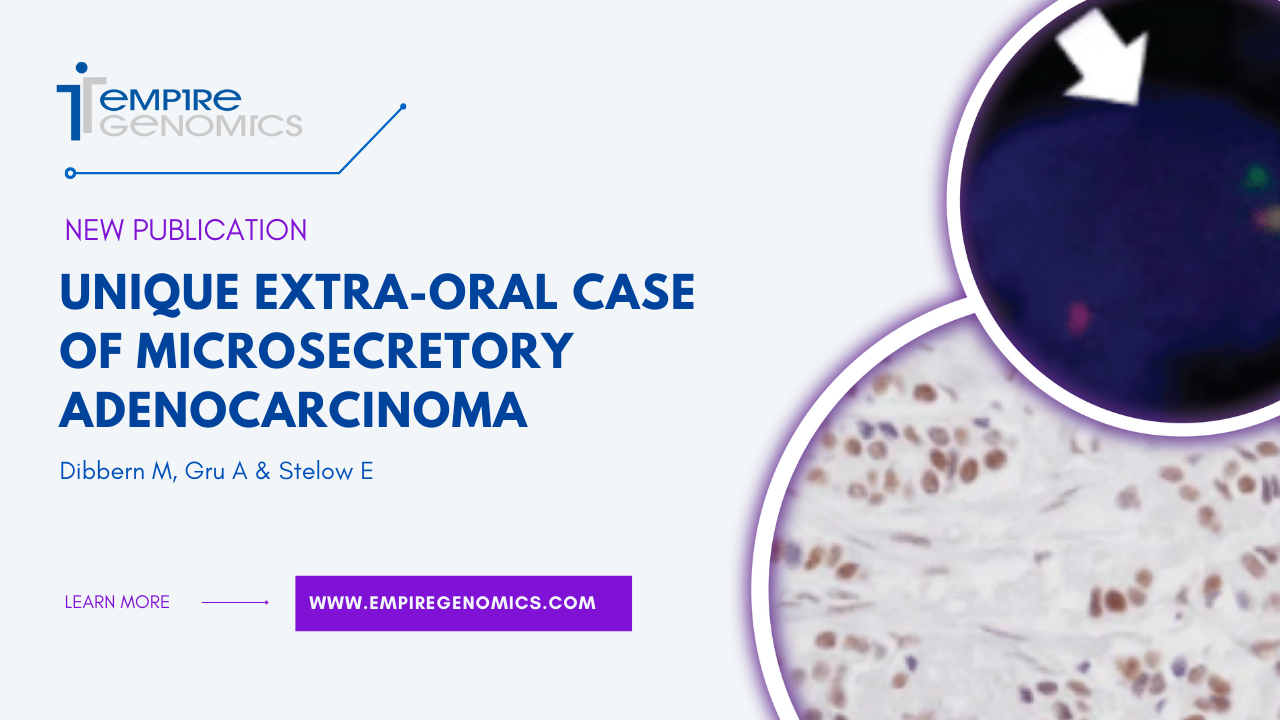
Unique extra-oral case of microsecretory adenocarcinoma
Microsecretory adenocarcinoma (MSA) is a salivary gland tumor that usually presents as a painless mass in the oral cavity. It was first described in case literature in 2019, with 24 definitive cases reported since its initial description. Of these cases, there is only one known to have arisen outside of the oral cavity; that case arose in the parotid gland. In this case, the authors present histomorphologic,..
Novel Entrectinib Resistance Mechanism Identified in NSCLC
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a genetically heterogeneous disease. In approximately 2% of NSCLC cases, the primary oncogenic mutation is a chromosomal rearrangement involving ROS1 (c-ros oncogene 1), where one of many diverse gene partners fuses to the 3’ kinase domain of ROS1 and results in the constitutive activation of the ROS1 receptor tyrosine kinase...

BIOCARE MEDICAL Acquires Empire Genomics, Expanding Molecular Portfolio to Over 1 Million Biomarkers and Adding Rapid Biomarker Development to Lead Cancer Research
Biocare Medical, a leading provider of innovative, automated immunohistochemistry (IHC) and FISH (Fluorescent in situ hybridization) instrumentation and reagents, announces the acquisition of Empire Genomics, a market leader in molecular biomarkers to aid in cancer research and diagnostics...

CLIP1-LTK Fusion Identified as New Druggable Target in Lung Cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common form of lung cancer and a leading cause of death worldwide. Fortunately, the survival rate for NSCLC patients has been increasing, in large part due to advances in targeted molecular and immunotherapies. Somatic mutations and gene fusions that alter the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)/RAS/REF pathway are frequent..

CDR2L Alterations in HER2+/HR- Breast Cancers Elicit Autoimmunity
Paraneoplastic syndromes are rare disorders co-occurring with cancer that are not directly related to the local presence of tumor cells, but result from the generation of autoantibodies, cytokines, hormones, or peptides in response to the malignancy. These syndromes have complex manifestations that can affect multiple organ systems, including the neurological, dermatological, gastrointestinal, endocrine, hematologic, and cardiovascular systems; neurologic presentations are most common...

Only a Minority of Gene Fusions Result in Osimertinib Resistance
Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which represents 80-85% of lung cancer cases, has drastically changed over the past two decades with the development of molecularly targeted therapies, including tyrosine kinase inhibitors...

Invasive ductolobular carcinomas have a ductal origin
Modern classification of mammary tumors depends on both histomorphology and molecular analyses. The most common histological type of breast cancer, accounting for approximately 80% of breast carcinoma cases, is invasive ductal carcinoma, classified as invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (IBC-NST) by the fifth edition of the WHO Classification of Tumors of the Breast. ..

Dusp4 needs help to trigger breast cancer tumorigenesis
The aggressive basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) subtype, which strongly correlates with triple-negative (ER- PR- HER2-) breast cancers, comprises 15-20% of all breast cancer cases and has a poor prognosis, largely resulting from a lack of a molecularly-targeted treatment regimen. Loss of control of signaling pathways frequently triggers tumorigenesis, and molecules involved in these signaling pathways are frequent molecular treatment targets. ..

Proteomic differences between squamous cell carcinomas from rare and common primary sites
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which develops in the top layer of the epithelium, and adenocarcinoma (AC), which develops in glandular epithelium cells, are two of the primary histological subtypes of carcinoma...

Amplification of 1q21 Linked to Poor Outcomes of Daratumumab-Based Treatments in Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a genetically heterogeneous disease, and this genetic heterogeneity can contribute to varied clinical responses and survival outcomes among patients. One of the most common cytogenetic abnormalities, occurring in around 40% of newly diagnosed MM cases and up to 70% of relapsed/refractory MM cases,..

Cerebral amyloid angiopathy alters endothelial gene expression patterns
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in older adults. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), which is characterized by the deposition of β-amyloid (Aβ) peptides within cerebral blood vessels, co-occurs with AD in 85-95% of AD cases and is an independent contributor to AD dementia...

PROTAC resistance in cancer cells is mediated by MDR1 drug efflux activity
Selectively inhibiting protein function through proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) has emerged as a novel cancer therapeutic strategy. PROTACs are small molecules with two active domains that bind to an E3 ubiquitin ligase and a protein of interest, which results in the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of the protein of interest...

Known cancer driver mutations found in endometrial polyps at low allelic frequencies
Endometrial polyps (EMPs) are localized overgrowths of endometrial tissue that are composed of endometrial glands, stroma, and blood vessels. The reported prevalence of EMPs increases with age and ranges from 8-35%, depending on the population studied. EMPs are generally considered to be benign, with risk of malignancy around 3%. However, EMPs have been associated with several endometrial cancers...

Loss of chromosome Y linked to AML and clonal hematopoiesis
Mosaic loss of chromosome Y (mLOY) is the most common form of clonal mosaicism and is recurrent in the blood cells of adult males. This chromosome alteration typically increases with age and has been linked with aging-related diseases including clonal hematopoiesis (CH), in which a single hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) gives rise to a genetically distinct subpopulation of peripheral blood or bone marrow cells, and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). ..

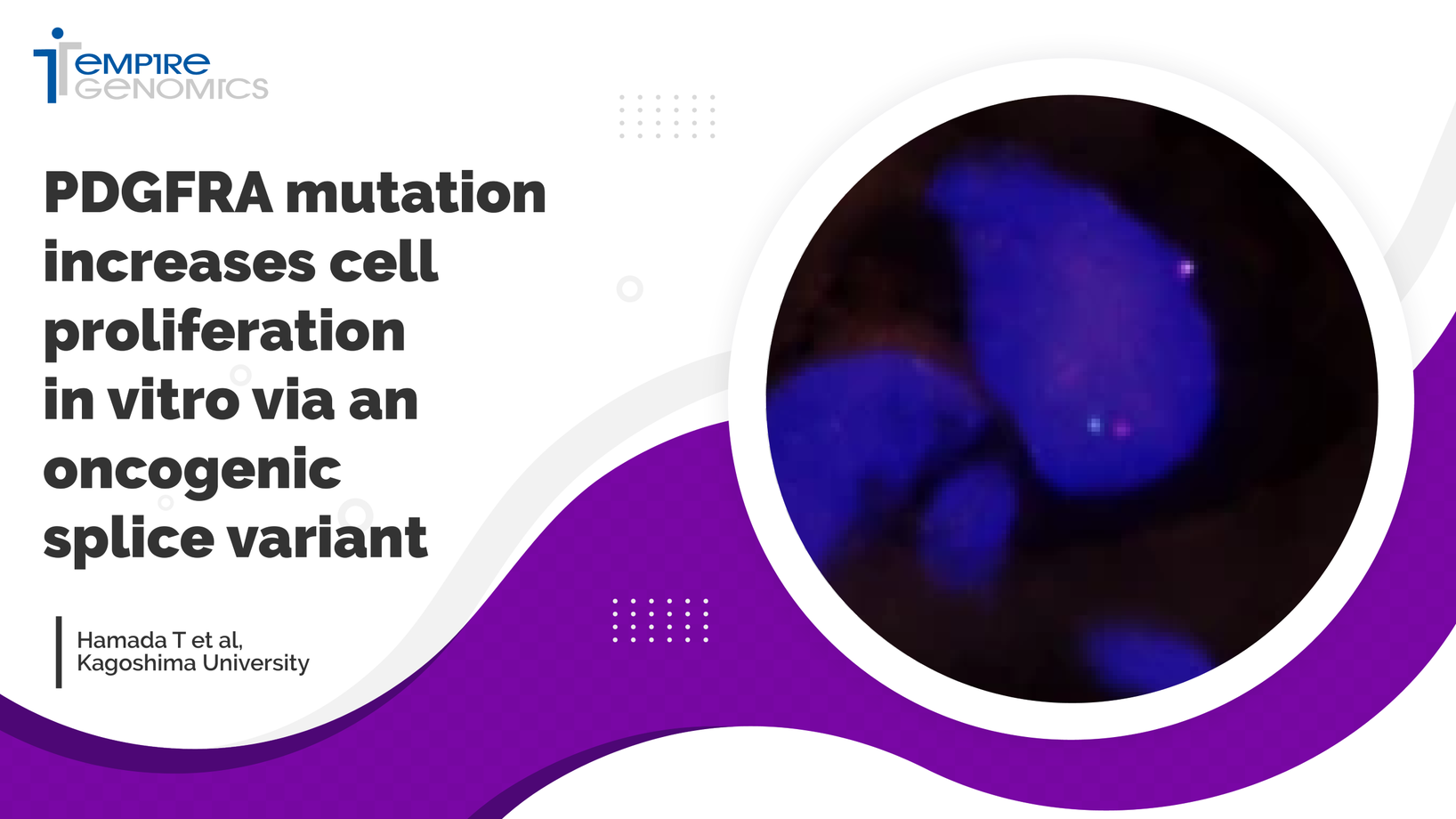
PDGFRA mutation increases cell proliferation in vitro via an oncogenic splice variant
The era of personalized medicine and genome-based cancer therapies has been accelerated by next-generation sequencing technologies, which allow for the identification of gene variants with clinical implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and patient care. However, many newly identified variants have yet to be linked to disease, and these are referred to as variants of uncertain significance (VUS)...
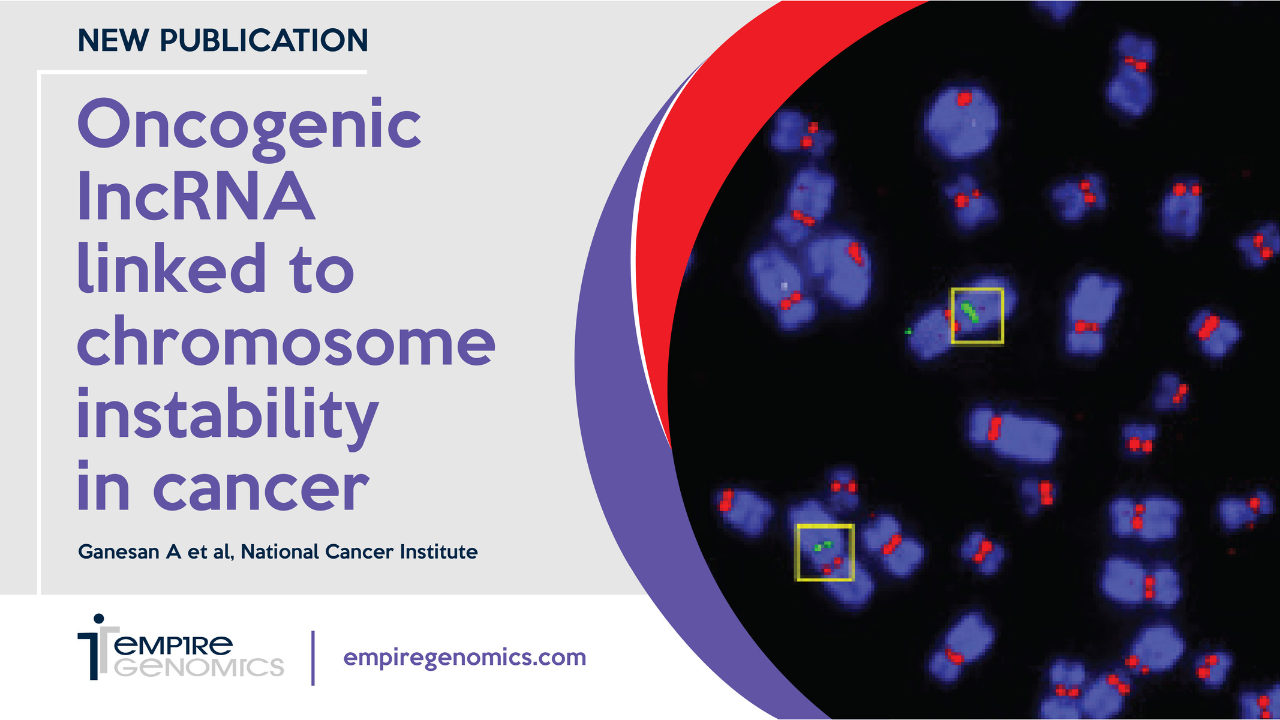
Oncogenic lncRNA PCAT2 linked to chromosome instability in cancer
hromosome breaks and translocations are often critical factors in tumorigenesis and cancer progression. One primary contributor to these types of chromosomal instability is the mis-regulation of histone proteins. Histones are responsible for packaging the human genome into chromatin and can be divided into five main families: H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4...
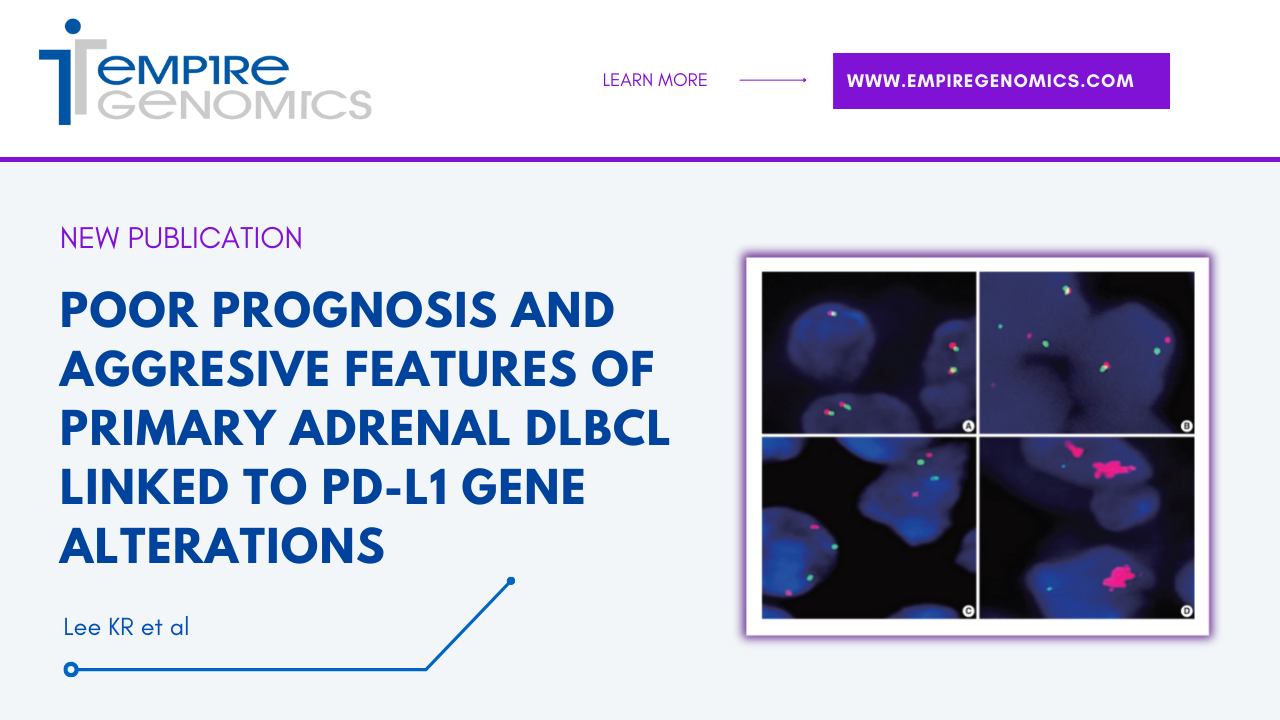
Poor prognosis and aggressive features of primary adrenal DLBCL linked to PD-L1 gene alterations
Primary adrenal (PA) lymphoma is extremely rare, accounting for less than 1% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas, yet is very aggressive and has a poor prognosis, with a general survival time of less than one year. In most cases, PA lymphomas are derived from B cells, with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) being the most common phenotype...
Empire Genomics Welcomes Andre Lubarsky as US Sales Director
July 20th, Buffalo, NY – Empire Genomics, a company that develops high-quality molecular probes for fluorescent and chromogenic in situ hybridization testing, has selected Andre Lubarsky to initiate the new North American business development strategy as Director of Sales. Andre is a seasoned sales director, most recently with System Biosciences, Inc., who will now be leveraging his experience to develop and execute key growth sales strategies in the United States and North America...

SUCLG2 proposed as biomarker in pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma
Pheochromocytoma, a neuroendocrine tumor of the adrenal medulla, and paraganglioma, a tumor derived from neural crest progenitor cells outside the adrenal gland, have a strong genetic basis, with up to 40% of cases displaying germline mutations and another 25-30% carrying a somatic mutation. ..

Point mutation causes dramatic shift in HIV-1 integration sites
Retroviruses, such as the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1), insert a copy of their genome into the host cell genome during a process called integration. This allows retroviruses to persist indefinitely in the infected cell as a provirus. During integration, the virally encoded integrase (IN) protein binds to various host factors that likely act as a tether between the viral IN protein and the host chromatin at the integration site...

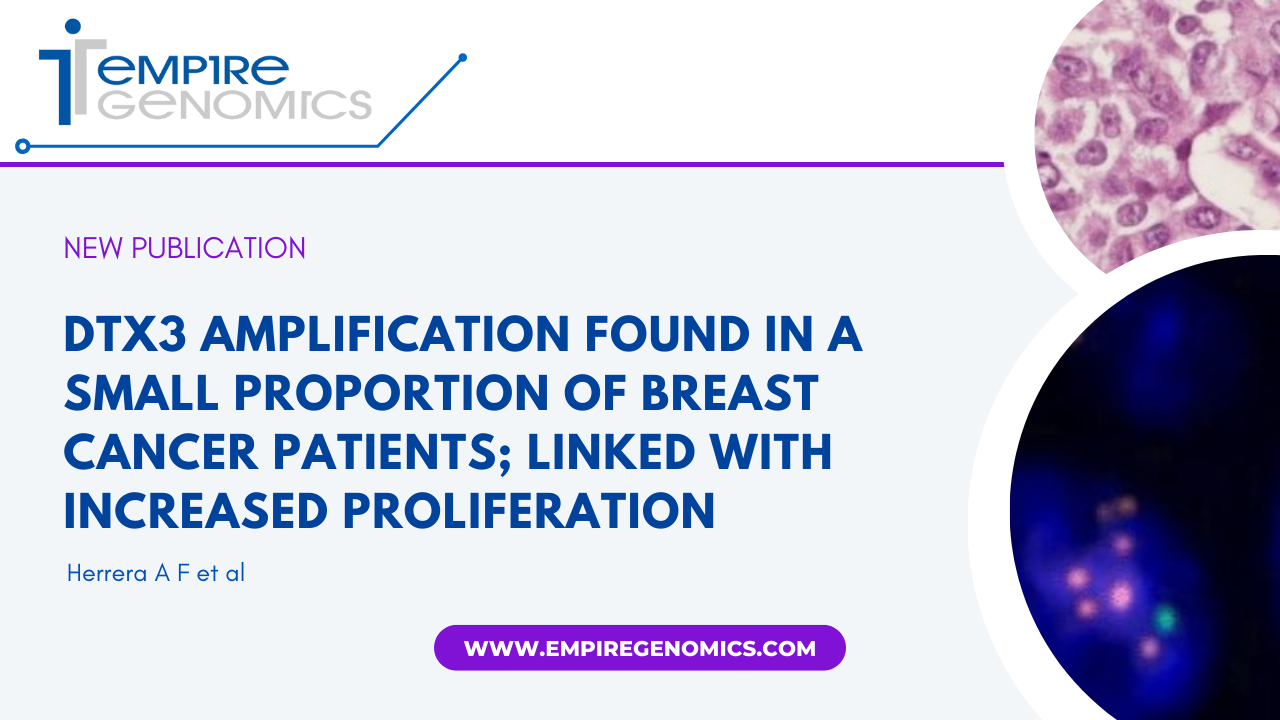
DTX3 amplification found in a small proportion of breast cancer patients; linked with increased proliferation
The degree of cell proliferation is one of the most powerful prognostic features in breast cancer. Deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 3 (DTX3), a member of the Deltex family, is located on 12q13.3 and is involved in neurogenesis and Notch signaling. DTX3 has been suggested as a potential driver gene of cell proliferation in luminal subtypes of breast cancer and has been associated with poor prognosis. However, studies of DTX3 in different cancers have found different results; in esophageal cancer, DTX3 was associated with reduced proliferation of tumor cells, and in colorectal cancer, DTX3 was proposed as an endogenous control gene for gene expression analyses...
Plott syndrome caused by an interchromosomal insertion
Plott syndrome, or familial congenital bilateral laryngeal abductor paralysis, was first described by Plott and colleagues in 1964 and has been reported twice since that time. Clinical expression has been limited to male children, and inheritance patterns have suggested Plott syndrome to be an X-linked recessive disorder. However, no conclusive genetic or chromosomal aberration has been reported to date, and no genetic tests have been conducted on any of the affected families. In this case, the authors report a new family with Plott syndrome and present data to suggest that Plott syndrome is caused by a 404kb fragment inserted into the intergenic chromosomal region Xq27.1...

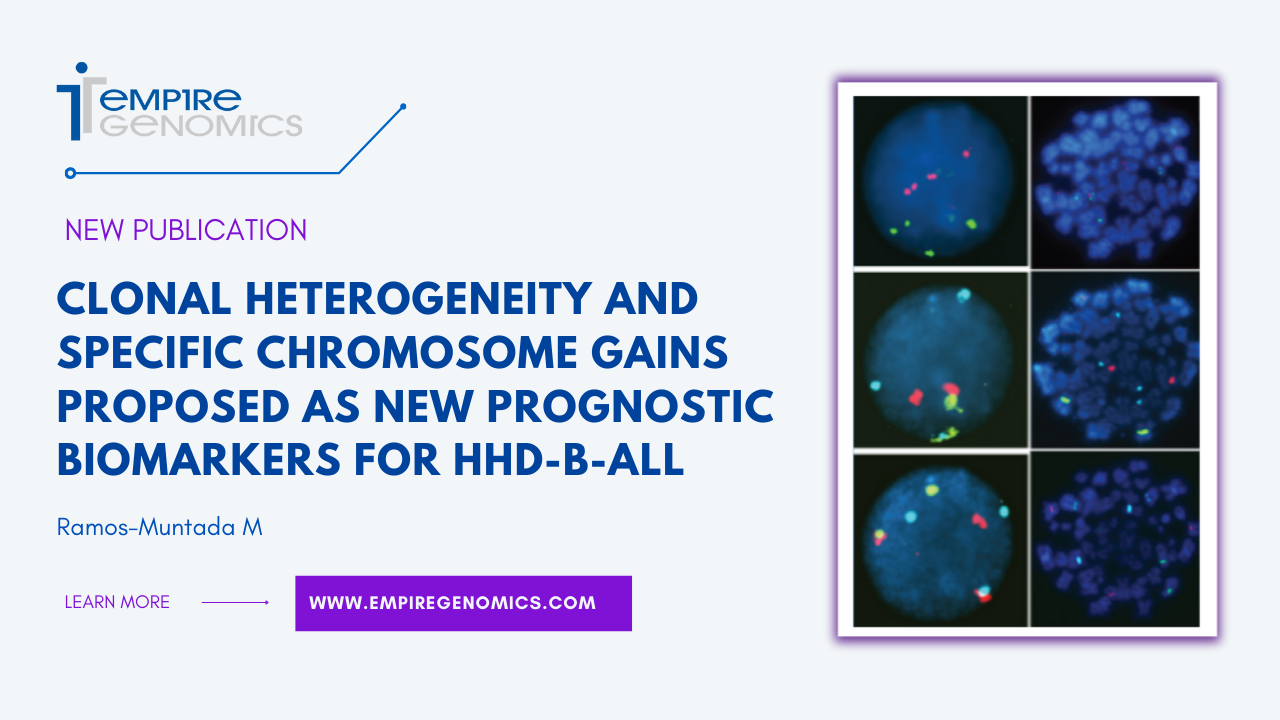
Clonal heterogeneity and specific chromosome gains proposed as new prognostic biomarkers for HHD-B-ALL
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the most common childhood cancer, features a substantial subgroup of patients with chromosomal gains (hyperdiploidy). Patients with a modal chromosome number >50 (high hyperdiploidy; HHD) account for nearly 30% of B-ALL cases and typically have a more favorable prognosis. Although HHD represents an important prognostic factor in childhood B-ALL, the specific chromosome gains that most contribute to a favorable clinical outcome have yet to be established...
Unique Extra-Oral Case of Microsecretory Adenocarcinoma
The patient originally presented for treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. A painless mass in her right external ear canal was identified, and further examination revealed an obstructing, friable lesion causing cerumen impaction. ..
Avelumab (Anti-PD-L1) in Relapsed/Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is characterized by the presence of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg tumor cells. In cHL, these malignant cells become surrounded by an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment composed largely of reactive immune cells. ..

First Report of an APP Locus Triplication Causing Early-Onset CAA and AD
The accumulation of amyloid-β precursor protein (Aβ) plaques is characteristic of both cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and Alzheimer disease (AD). Duplications of the amyloid-β precursor protein (APP) gene, which is located on 21q21.3, have been linked to early onset CAA and/or early onset AD...

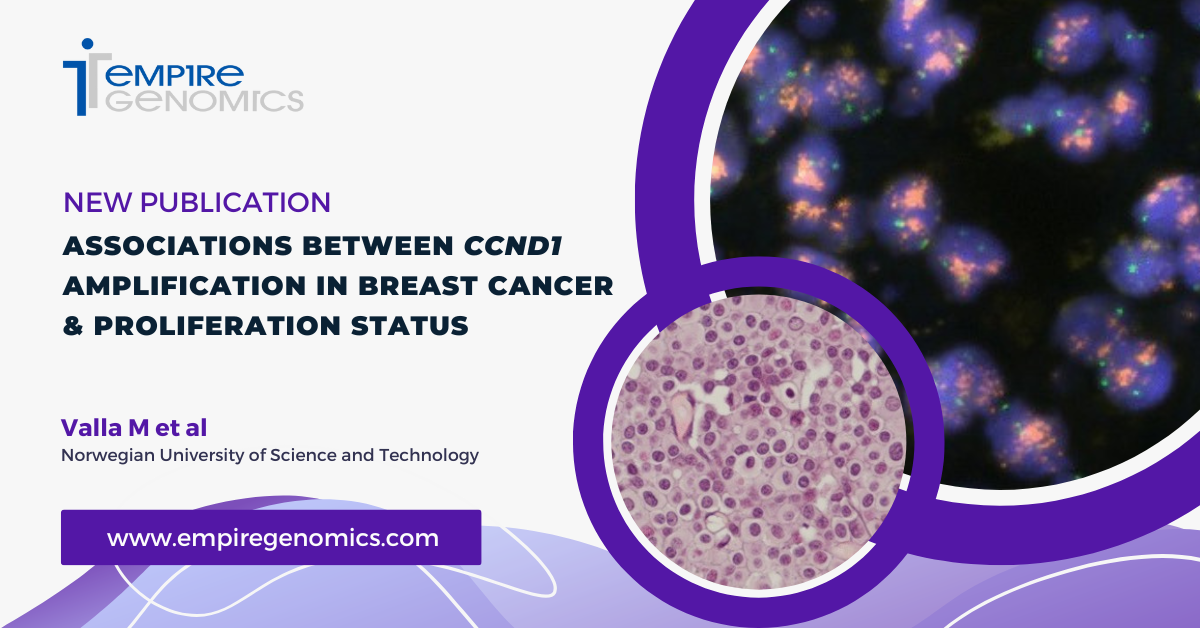
Associations Between CCND1 Amplification in Breast Cancer & Proliferation Status
Breast cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease that differs greatly between patients. As such, there is a need for new biomarker discovery that would allow for individualized diagnoses, treatments, and prognoses for breast cancer patients. In this study, the authors assessed the ability of CCND1 amplification to serve as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer...
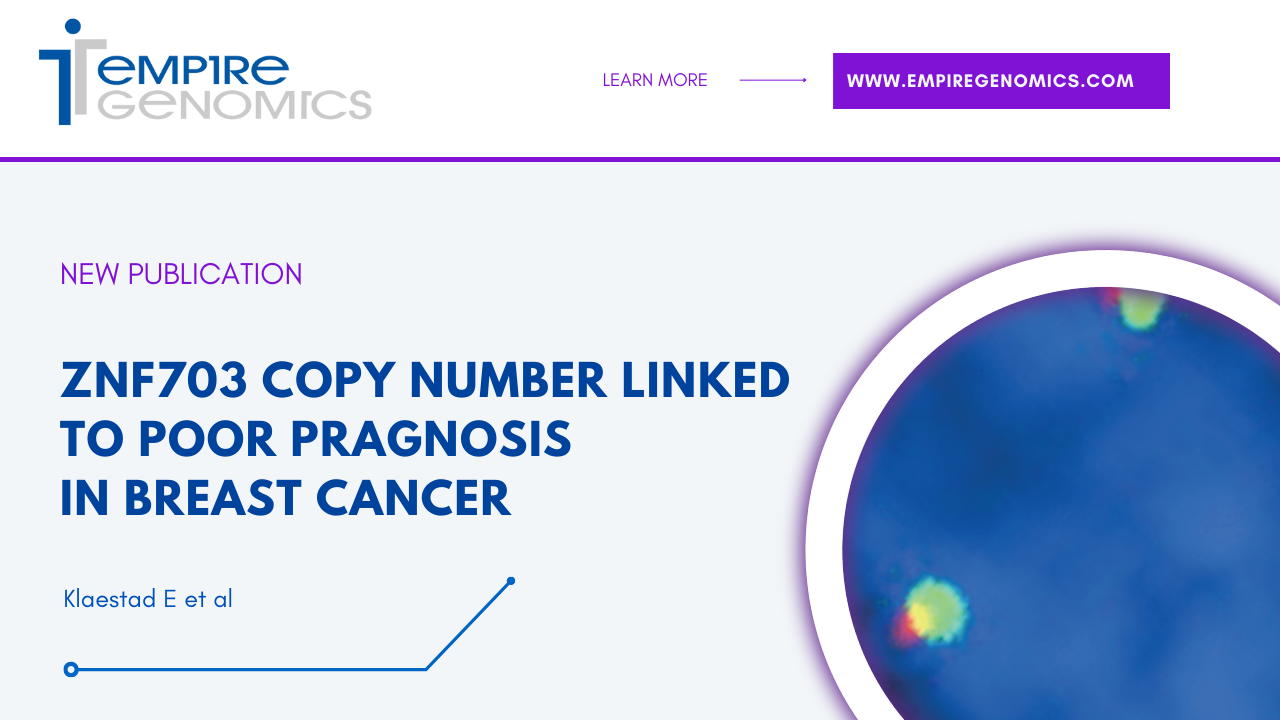
ZNF703 Copy Number Linked to Poor Prognosis in Breast Cancer
Among patients with breast cancer, luminal subtypes are the most common. Differences in prognosis have been demonstrated between the luminal subtypes, ranging from patients with an excellent prognosis to those who require much more aggressive treatment. ..
PTHrP drives pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis and reveals a new therapeutic vulnerability
Pancreatic cancer is notorious for its rapid clinical course. It’s highly aggressive, invasive, and after metastasis, is nearly always fatal. Most patients will die within a year of diagnosis. Treatment options are limited, largely because the molecular pathways driving the disease are still unknown. ..

Superresolution microscopy reveals linkages between ribosomal DNA on heterologous chromosomes
The spatial organization of the nucleus is startlingly intricate. Chromosomes occupy distinct territories, and can form complex intra- and inter-chromosomal connections. However, these associations, especially those of the inter-chromosomal variety, are still mysterious in frequency and function. ..

Clinicopathological Characterization of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Young Adults: a contemporary update and review of literature
A continuous challenge for cancer researchers is conducting analyses in age groups where cases are limited. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that occurs in individuals of all ages, but is far more prevalent in older patients. Because of this, research on young adult and childhood RCC (in particular, morphological and genetic characterization studies) has been scant. ..

Hydropic leiomyoma: a distinct variant of leiomyoma closely related to HMGA2 overexpression
Uterine leiomyoma (ULM) is the most prevalent benign tumor of the female reproductive system, occurring in up to 70% of pre-menopausal women. Several different subtypes have been identified, including hydropic leiomyoma (HLM). Certain aspects of HLM’s morphology make it difficult to identify – particularly, cases with extensive hydropic change can hide features typical of leiomyoma, making diagnosis tricky...

Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with t(7;21)(p22;q22)
Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML) accounts for about 25% of childhood cancer cases. While survival rates have risen dramatically in the past few decades, 30% of patients still experience relapse. Fortunately, recent studies have uncovered a variety of genetic abnormalities specific to the disease that both (A) provide important hints about its pathogenic/clinical course and (B) may serve as therapeutic targets for future treatment...

Analysis of NTRK Alterations in Pan-Cancer Adult and Pediatric Malignancies: Implications for NTRK-Targeted Therapeutics
We now understand that cancer is a disease rooted in genomic breakdown. But when analyzing a patient’s genome, not all mutations contribute equally to disease. Further complicating things is the fact that, even after a gene’s role in cancer development is clearly established, only certain alterations can be targeted by current therapies. Therapeutically targetable mutations, therefore, are needles in the haystack for cancer researchers – which explains the recent excitement around the NTRK gene family...

Somatic and germline genomics in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
The interplay between hereditary and somatic mutations in cancer development has been a difficult relationship for oncologists to unravel. While we now know that some cancers are indeed heritable, we don’t always know to what degree. Pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is one such disease, with a well-documented but still ambiguous hereditary component. A new study out of St. Jude’s Research Hospital – Somatic and germline genomics in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) - expanded on the complex genetics of the disease. ..

Infantile NTRK-Associated Mesenchymal Tumors
Infantile fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors are the second most prevalent type of soft tissue neoplasms in pediatric patients < 1 years old. Although the majority of these tumors are either benign or low-grade, there are certain subtypes with a higher tendency toward malignancy. Congenital infantile fibrosarcoma (CIFS) is one such high-risk group. CIFS patients, who are nearly always less 2 years old, present with morphologically ambiguous tumors that can resemble a range of other infantile neoplasms of varying clinical course, including myofibroma/myofibromatosis, lipofibromatosis and fibrous hamartoma of infancy, primitive myxoid mesenchymal tumor of infancy (PMMTI), and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)...

Alterations in ALK / ROS1 / NTRK / MET Drive a Group of Infantile Hemispheric Gliomas
Gliomas are rare brain tumors that can affect individuals of all ages. While studies are plentiful on pediatric and adult gliomas, infant cases are historically understudied – an unfortunate fact, considering central nervous system tumors are most common (and deadly) in this age group. This research team sought to account for that lack of data by cytogenetically analyzing infant glioma samples collected between 1986 and 2017. The team was able to divide these tumors into three genetic subtypes that were tightly tied to clinical outcome. Additionally, they found that many of the tumors harbored just a single genetic aberration, evidence that infant gliomas are usually single driver tumors...